Table of Contents
- Key Points
- Timber Support in Different Mine Areas
- Survey Note: Detailed Analysis of Timber Support in Mines
- Introduction to Timber Support
- Side Support: Preventing Wall Collapses
- Support of Roadways: Ensuring Access and Ventilation
- Clearing Up Heavy Roof Falls: Emergency Response
- Systematic Timbering: Standardized Safety Measures
- Withdrawal of Supports: Safe Removal Practices
- Comparative Analysis: Timber vs. Modern Alternatives
- Table: Summary of Timber Support Applications
- Conclusion
Key Points
- Timber support is commonly used in coal mines to prevent collapses, especially in side support, roadways, and after roof falls.
- Research suggests timber is cost-effective and elastic, suitable for various mining conditions, but modern alternatives like rock bolting are increasingly used.
- It seems likely that systematic timbering and safe withdrawal methods are crucial for mine safety, with specific techniques varying by mine conditions.
Timber Support in Different Mine Areas
Overview
Timber support involves using wooden structures to ensure safety and stability in underground mines, particularly coal mines. It is vital for preventing collapses and maintaining access.
Side Support
Timber is used to support mine walls, especially where rock is weak. Wooden laggings between props and pillars, and angled props, help resist side pressure.
Roadway Support
For mine roadways, timber props and bars support the roof, often with cogs at junctions, ensuring ventilation and access are maintained.
Clearing Heavy Roof Falls
After roof collapses, timber is used for temporary and permanent supports, allowing safe debris removal and re-establishing stability.
Systematic Timbering
This is a standardized support pattern, mandatory in areas like bord and pillar workings, ensuring consistent safety as per mine manager rules.
Withdrawal of Supports
Timber supports are removed safely using tools like the Sylvester prop-withdrawer, with anchor props for stability, crucial in depillaring areas.
Survey Note: Detailed Analysis of Timber Support in Mines
Timber support remains a cornerstone of underground mining operations, particularly in coal mines, due to its cost-effectiveness and adaptability to various geological conditions. This section provides a comprehensive examination of its application in different mine areas, drawing from historical practices, current standards, and recent insights.
Introduction to Timber Support
Timber support refers to the use of wooden structures, such as props, bars, and cogs, to provide stability and prevent collapses in underground mines. It is especially prevalent in coal mining, where the rock conditions often require additional reinforcement. The elasticity and strength of long-grained timber, such as sal (Hindi-Sakhwa) props, make it suitable for supporting mine roofs and walls, withstanding pressures up to 500 pounds per square foot (Mining Timbers | Sell Lumber Corporation). Despite advancements like rock bolting, timber remains relevant, particularly in developing regions where it is readily available and affordable.
Side Support: Preventing Wall Collapses
Side support is critical in areas where mine walls are weak or fractured, preventing them from caving in and obstructing roadways. Techniques include:
- Placing wooden laggings tightly between vertical props and pillars to distribute side pressure.
- Setting props at an angle of 14° to 20° off the vertical, with feet sunk into the floor, to better resist lateral forces.
- Reinforcing with additional bars or stretchers nailed to props, though this may reduce roadway height, making it less advisable in low-height areas (less than 2 meters) used by basket loaders.
This method is detailed in resources like Types of Mine Supports: Timber, Iron and Steel | Rock Mechanics | Mining Technology, highlighting its importance in maintaining structural integrity.

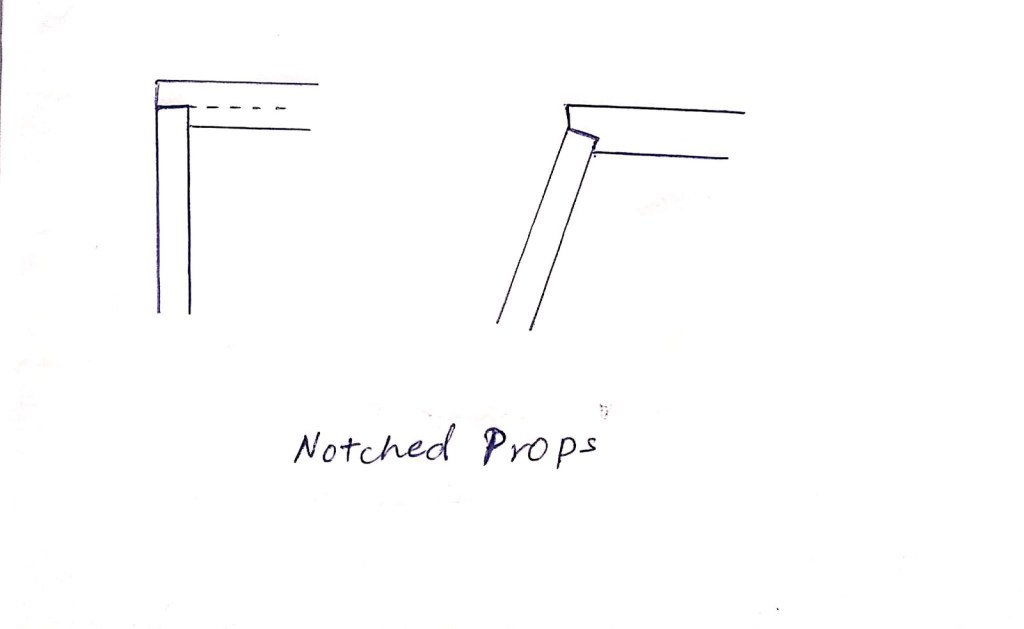
Support of Roadways: Ensuring Access and Ventilation
Roadways are essential for miner access and ventilation, requiring robust support to prevent roof falls. Common practices include:
- Erecting bars in holes of coal pillars, tightened against the roof with wooden laggings, at intervals of 2 to 3 meters.
- Using timber props to support bars when coal pillars are weak, especially in fault zones.
- Employing cogs and bars for wider junctions, ensuring no props are placed where they could be dislodged by moving equipment.
This approach is supported by Timber Support in Underground Mining – 911Metallurgist, which notes the necessity of such supports for operational continuity.
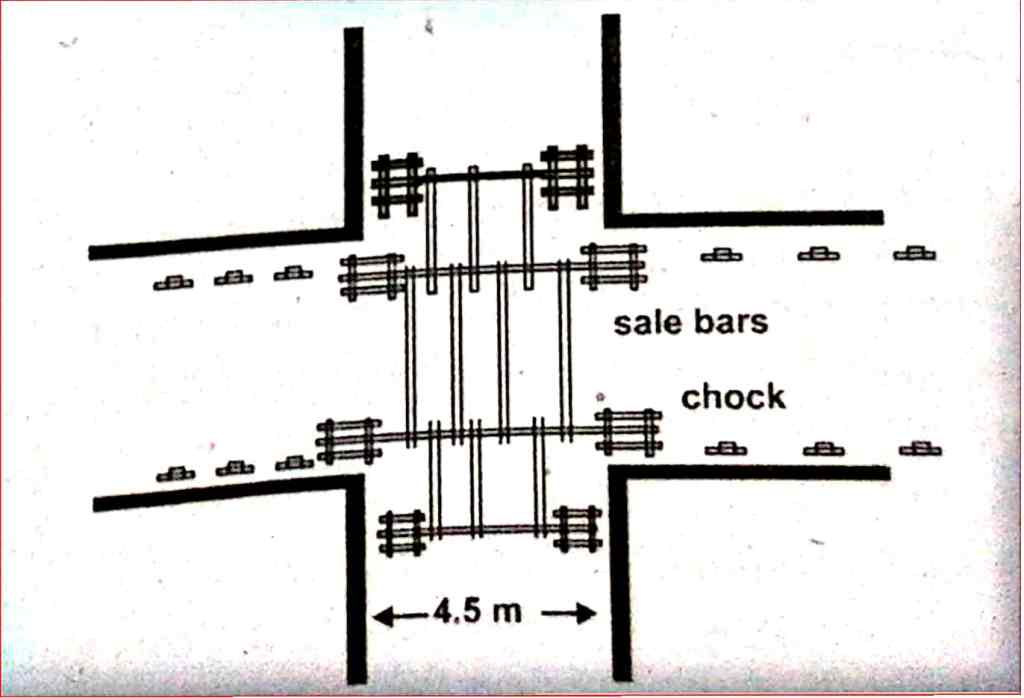
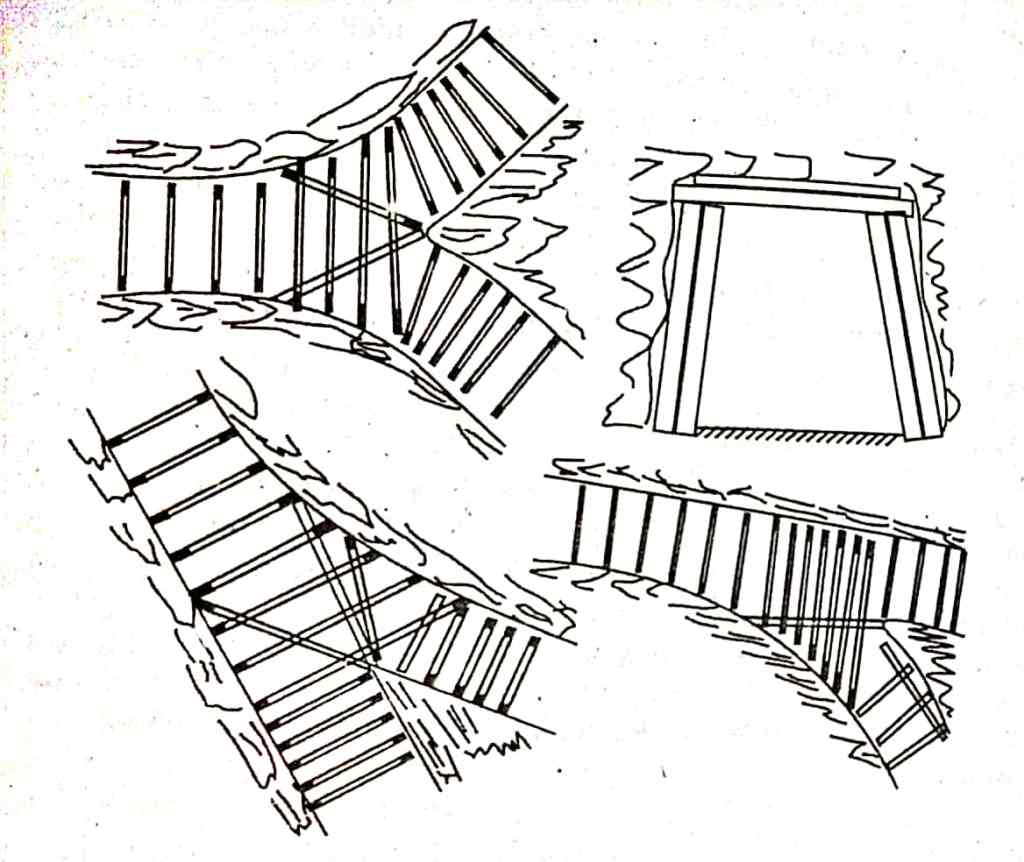
Clearing Up Heavy Roof Falls: Emergency Response
Heavy roof falls pose significant risks, potentially blocking ventilation and stranding miners. Timber plays a key role in safely clearing debris:
- Experienced timber men work from safe places, erecting sets of props and bars after dressing loose roof rock.
- Temporary props with thick sole plates and top lids are used on debris for immediate roof support, allowing debris removal and packing in nearby galleries or along haulage roads.
- Permanent supports, like cogs and bars, are then installed, especially in important areas, sometimes using brick walls and corrugated galvanized iron (C.G.I.) sheets for long-term stability.
This process, detailed in the provided text from February 23, 2020, underscores the importance of timely and safe re-supporting to restore mine operations.

Systematic Timbering: Standardized Safety Measures
Systematic timbering involves erecting supports according to a specified pattern, approved by the Directorate of Mines Safety, and is essential in areas like bord and pillar workings, longwall faces, and disturbed ground. Key aspects include:
- Specifying types of supports (cogs, props, bars) in the systematic timbering order, handed to supervising officials and posted in the mine.
- Ensuring additional supports are erected as needed, maintaining a consistent safety framework.
This practice is highlighted in Anthracite Mine Timbering Methods – Underground Miners, which emphasizes its role in preventing roof falls through systematic placement.
Withdrawal of Supports: Safe Removal Practices
When timber supports are no longer needed, safe withdrawal is crucial to avoid accidents. Methods include:
- Using safety prop-withdrawers like the Sylvester prop-withdrawer, which provides a controlled release, often with chains or flexible wire ropes in depillaring areas.
- Fixing anchor props or bars in coal pillars to ensure stability during withdrawal, preventing dislodgement of other supports.
This is supported by Underground Mine Timbering & Support – 911Metallurgist, noting the legal prohibition on hammering for removal.

Comparative Analysis: Timber vs. Modern Alternatives
While timber is traditional, modern mining increasingly adopts alternatives like rock bolting, which offers longer durability (20-40 years) and reduced excavation costs (Timber Support in Underground Mining – 911Metallurgist). However, timber remains relevant in cost-sensitive operations, with ongoing research into its integration with new technologies for enhanced safety.
Table: Summary of Timber Support Applications
| Application | Purpose | Key Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Side Support | Prevent wall collapses | Laggings, angled props, additional bars |
| Roadway Support | Maintain access and ventilation | Bars, props, cogs at junctions |
| Clearing Roof Falls | Safe debris removal and re-supporting | Temporary props, permanent cogs and bars |
| Systematic Timbering | Standardized safety in specific areas | Patterned support erection, additional as needed |
| Withdrawal of Supports | Safe removal of used supports | Prop-withdrawers, anchor props |
This table encapsulates the diverse roles of timber support, reflecting its versatility across mine operations.
Conclusion
Timber support is integral to mining safety, with applications ranging from side and roadway support to emergency responses and systematic practices. Its continued use, alongside modern alternatives, highlights its enduring relevance, supported by regulatory frameworks like those from MSHA (Regulations | Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA)).
Key Citations
- Types of Mine Supports: Timber, Iron and Steel Rock Mechanics Mining Technology | Mine Portal
- Timber Support in Underground Mining – 911Metallurgist
- Mining Timbers | Sell Lumber Corporation
- Anthracite Mine Timbering Methods – Underground Miners
- Underground Mine Timbering & Support – 911Metallurgist
- Regulations | Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA)







Leave a comment